
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has proven to be one of the leading business destinations. Its good uae freezone corporate tax regime has helped in this. The freezone corporate tax framework in the UAE has evolved significantly in the last few years with the introduction of a federal corporate tax regime in 2023. Against this backdrop, the Free Zones of the UAE have emerged as a critical component of the country's economic framework. They offer businesses a unique set of benefits that are not available elsewhere, such as tax exemptions, streamlined regulations, and world-class infrastructure. This overview will go into depth on the intricacies of the UAE's freezone corporate tax system, focusing on the critical role that Free Zones play in economic growth and foreign investment.
Here is the latest update on UAE Corporate Tax for Freezones
Free Zones in UAE are geographic areas designated with special regulatory and economic privileges given to businesses to attract foreign investment and promote economic diversification. The zones function according to their rules and regulations, which vary from those applied to businesses operating outside the zones. Major free zone functions include:
What is the Freezone Corporate Tax Regime in UAE?
In the UAE, a free zone person means businesses that are set up and run in one of the country's free zones. These businesses enjoy special tax breaks and rules that help attract foreign investment. This term can include both individual business owners and companies.
Natural Person
A natural person is a natural person in the UAE corporate tax context, who has business activities and generates business income. These persons may have to pay corporate tax as well if their business income crosses a particular threshold. More specifically, business income by a natural person exceeding AED 1 million must be subjected to corporate tax, whereas employment or investment income, not requiring any license, are not within the purview of tax.
Juridical Person
A juridical person is a legal entity which may be a corporation, partnership or limited liability company, recognised by law as having rights and obligations. All juridical persons in the UAE are liable to corporate tax on their taxable income, comprising profits arising from business carried out within the country.
What is Tax Applicability for Various Types of Entities?
The UAE corporate tax is applicable to different types of entities:
Special provisions under the UAE corporate tax regime have been provided for the free zone companies:
The UAE applies different corporate tax rules for Mainland and Free Zone businesses. Here are the major differences :
| Category | Mainland | Free Zones |
| Corporate Tax Rates | A 9% tax rate is applied to any income above AED 375,000. | Many Free Zone businesses are tax-free on "Qualifying Income" by meeting certain criteria. |
| Tax on Qualifying Income | Any income above AED 375,000 is taxed at the standard rate. | Likely exempted from tax on income generated from activities aligned with Free Zone objectives. |
| Activities Eligible for Tax Benefits | Can carry out activities anywhere in the UAE with no restriction. | Tax benefits apply to specific activities; non-permitted activities may be taxed at normal rates. |
| Trading Restrictions | Allowed to trade freely within the United Arab Emirates. | May face restrictions in Mainland trade; often need a local distributor or branch for Mainland sales. |
| Tax Compliance | Must follow FTA regulations; proper registration and auditing procedures are mandatory. | Must also follow FTA regulations; requirements are slightly easier if tax exemptions apply. |
Find out more by reading A Quick Guide to Corporate Tax on Mainland and Free Zones
Who Can Be a Qualifying Free Zone Person?
A Qualifying Free Zone Person is a business entity that has met certain criteria stipulated by the UAE Corporate Tax Law. For this to be so, the business entity must meet six essential conditions:
Qualifying Income denotes income that a Qualifying Free Zone Person derives from particular sources of activities that are eligible for a 0% corporate tax rate within the UAE Corporate Tax Law. This income is sourced through transactions and activities conducted within, or from, designated free zones.
Qualifying income for free zone persons relates to:
Qualifying Income Examples
Non-Qualifying Income Examples
Qualifying Activities and Non-Qualifying Activities in UAE Free Zones
To benefit from the 0% corporate tax rate as a Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP), businesses must meet specific conditions related to their activities and income sources:
Non-qualifying activities conducted by QFZPs are subject to the standard corporate tax rate of 9%. Any income derived from these activities will not benefit from the 0% rate, potentially impacting the overall tax liability of the business.
Certain activities are explicitly excluded from qualifying for the 0% corporate tax rate, including:
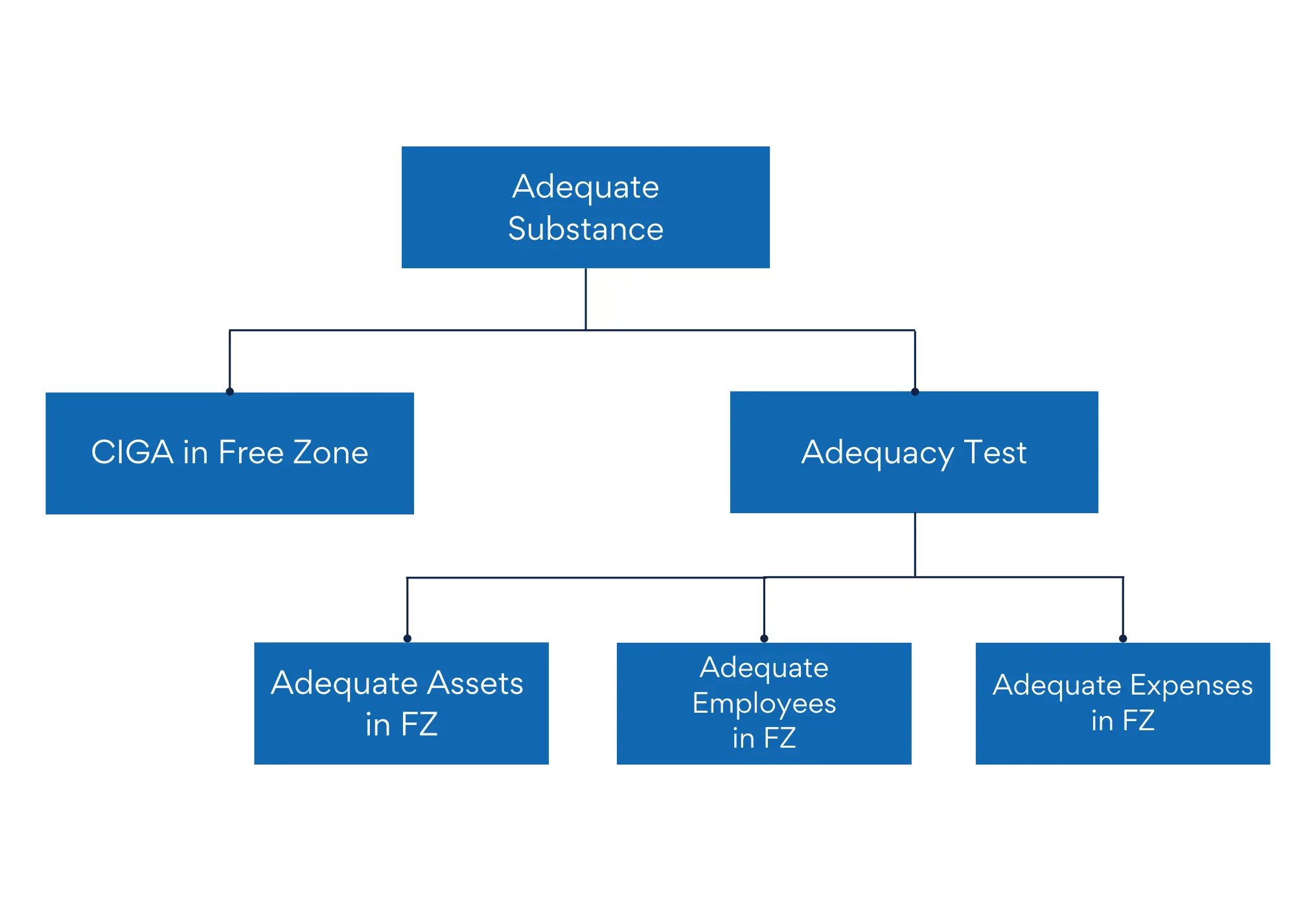
For having Adequate Substance in UAE, two regulations needs to be followed
Outsourcing Activities
Outsourcing Activities can be outsourced to a related party or a third party within the Free Zone, provided the Qualifying Free Zone Person maintains adequate supervision over the outsourced activities.
As permitted under the UAE freezone Corporate Tax Law and De Minimis requirement, Qualifying Free Zone persons may retain their 0 percent corporate tax on qualifying income should they have non-qualifying income; however their non-qualifying amount needs to be less than five percent of total revenue. Otherwise, their non-qualifying amount will be 5 million AED, or whatever is smaller.
This requirement is intended to:
Thresholds: The AED 5 million or 5% of total revenue whichever comes first, is the threshold of non-qualifying income for a QFZP.
Excluded from the calculation are:
If a qualifying freezone person's non-qualifying income during a tax period does not surpass 5% of their total income for that tax period, or AED 5,000,000 (5 million dh), (whichever is lower), then the de-minimis requirement will be satisfied.
| Example 1 | Example 2 | |
| Total Revenue | 1,20,000,000 | 80,000,000 |
| 5% of Total Revenue | 6,000,000 | 4,000,000 |
| Threshold | 5,000,000 | 5,000,000 |
| Satisfies for De-Minimis Requirement | No | Yes |
To calculate the 5% in De-Minimis Requirement
(Non-Qualifying Income ÷ Total Income) × 100
Free Zone Corporate Tax, is the tax levied by the Free Zone system that distinguishes between earnings of qualifying and non-qualifying income for Free Zone Business
Tax Rates and Thresholds
This system creates a competitive tax environment, particularly for small and medium businesses, by offering a tax-exempt zone for a portion of their profits.
Free Zone companies must register for corporate tax through the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) using the EmaraTax online portal. The steps are involved in the process:
Once registered, Free Zone entities have the following filing and reporting obligations:
Freezone Corporate tax in the UAE is calculated based on the net profit reflected in the company's financial accounts. To file tax returns and determine the amount of Corporate Tax owed, maintaining specific financial documents is essential. Here are the documents needed to prepare for filing Corporate Tax in the UAE:
Corporations and businesses operating in UAE freezones must adhere to specific deadlines for filing Corporate Tax. Here is a detailed timeline to help ensure compliance:
| Task | Description | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
|
Register with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) for Corporate Tax. |
Within 30 days of commencing business activities. |
|
|
Submit the annual Corporate Tax Return to the FTA. |
Within 9 months from the end of the financial year. |
|
|
Tax Payment |
Settle the payable Corporate Tax amount. |
Within 9 months from the end of the financial year |
|
Deregistration |
Submit a deregistration application if the business ceases operations. |
Within 30 days of ceasing business activities. |
|
Voluntary Disclosure |
Submit a voluntary disclosure for any errors in the Tax Return or Tax Assessment |
As soon as the error is discovered, preferably before notification of a Tax Audit |
|
Declaration Submission |
Submit any required declarations to the FTA |
As specified by the FTA, usually within the same timeframe as the Tax Return |
|
Notification of Change |
Inform the FTA of any changes requiring amendments to tax record information. |
Within 20 business days of the change occurring |
The UAE currently doesn't impose specific penalties related solely to the Free Zone corporate tax regime. However, the general UAE freezone corporate tax framework outlines penalties for non-compliance that apply to both mainland and free zone businesses. Here's what you need to be aware of:
|
No. |
Description of Violation |
Administrative Penalty Amount in AED |
|
1 |
Failure to keep required records and other information specified in the Tax Procedures Law and Corporate Tax Law. |
10,000 for each violation; 20,000 for repeated violations within 24 months. |
|
2 |
Failure to submit tax-related data, records, and documents in Arabic to the Authority when requested. |
5,000 |
|
3 |
Failure to submit a deregistration application in the allowed period. |
1,000 monthly, up to 10,000 |
|
4 |
Failure to inform the Authority of changes requiring amendment of tax record information. |
1,000 monthly, up to 10,000 |
|
5 |
Failure of the Legal Representative to notify the Authority of their appointment within the specified timeframes. |
1,000 |
|
6 |
Failure of the Legal Representative to file a Tax Return within the specified timeframes. |
500 monthly for the first 12 months; 1,000 monthly thereafter. |
|
7 |
Failure of the Registrant to submit a Tax Return within the specified timeframe. |
500 monthly for the first 12 months; 1,000 monthly thereafter. |
|
8 |
Failure to settle the Payable Tax. |
14% per annum on the unsettled amount, calculated monthly. |
|
9 |
Submission of an incorrect Tax Return. |
500, unless corrected before the deadline. |
|
10 |
Submission of a Voluntary Disclosure for errors in the Tax Return or Tax Assessment. |
1% monthly on the Tax Difference, from the due date until the disclosure is submitted. |
|
11 |
Failure to submit a Voluntary Disclosure for errors before notification of a Tax Audit. |
15% fixed penalty on the Tax Difference; 1% monthly on the Tax Difference. |
|
12 |
Failure to facilitate the Tax Auditor during a Tax Audit. |
20,000 |
|
13 |
Late submission or failure to submit a Declaration to the Authority. |
500 monthly for the first 12 months; 1,000 monthly thereafter. |
Free Zone businesses are to gain substantially from the corporate tax regime in the UAE:
Freezone Corporate Tax in UAE can be tricky but it’s important to get it right. Filing your taxes on time and correctly helps avoid penalties and keeps your business running smoothly. Reyson Badger’s team is here to help you with every step, making sure you meet all the rules and requirements. With our full guidance , you can focus on growing your business while we handle your tax needs. Trust Reyson Badger to keep your tax matters in order, so you can achieve your business goals without any worries.